How we shop for groceries has fundamentally altered without us realizing it. Weekly in-store shopping has been replaced by same-day delivery, smart shopping recommendations, and apps that track which items you forgot to purchase last time. In 2026, convenience will no longer be regarded as a luxury but an expectation. For businesses, this shift is not only about doing things differently but also about gaining visibility among the places where consumers spend their time. That is, on their mobile devices.
A recent report noted that, at the current growth rate, the global online grocery market will surpass $1 trillion by 2027, with mobile-first platforms leading the expansion. The industry has set standards in which features such as faster delivery times and AI-powered personalization are no longer nice-to-haves but essential requirements. If this is the case, it stands to reason that the question is not whether to develop a grocery mobile application, but how to develop one.
This is where grocery delivery app development comes into play. In this guide, we explain the components that go into creating a scalable, profitable grocery app that meets post-2026 consumer expectations without overwhelming you with overly complex technical details.
Why Grocery Delivery Apps One of the Fastest-Growing Digital Businesses?
Grocery delivery services grew rapidly and changed how people shop. What started as a pandemic convenience has become an ongoing behavior driven by speed, flexibility, and the convenience of delivery to your door. By 2026, this digital shift in consumer behavior will be reflected in the market’s considerable size and value.
- The global online grocery market was valued at approximately USD 664 billion in 2026, with analysts forecasting sustained growth well into the next decade as digital grocery adoption accelerates worldwide.
- The online grocery delivery services market is projected to reach approximately USD 1.12 trillion in total market size between 2024 and 2028, at a CAGR of 23–25%, according to Technavio analysis.
- The online grocery delivery segment alone reached a valuation of nearly USD 750 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow significantly by 2030, reflecting strong long-term demand for app-based grocery services.
These figures clearly demonstrate the growth potential in grocery delivery services and why grocery delivery app development is becoming a strategic priority for businesses looking to capture market share and meet evolving consumer expectations.
Business Models for Grocery Delivery Apps That Make Money
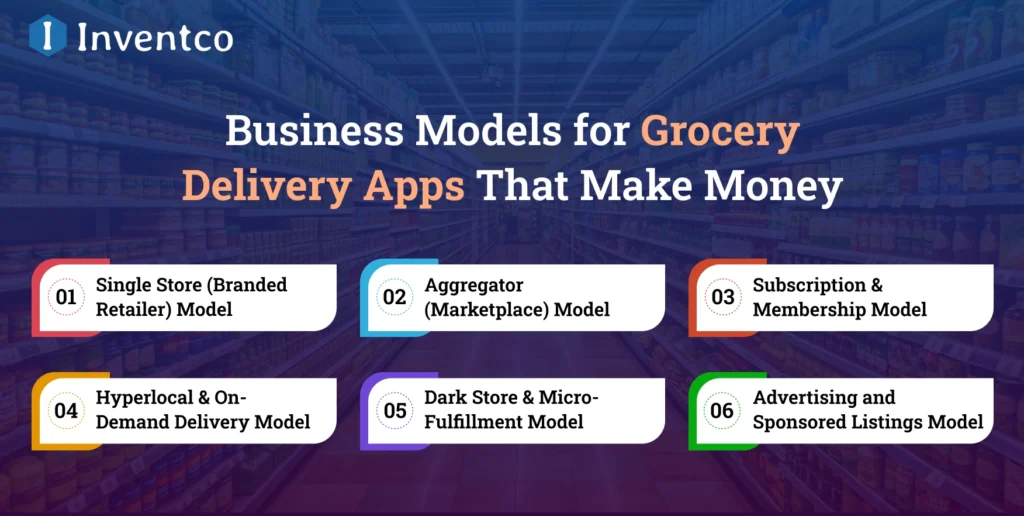
The construction of a grocery delivery platform depends on a single central tenet. Having the appropriate business model will make the grocery delivery platform highly profitable. In 2026, top grocery delivery apps will be scalable, operationally efficient, and generate positive cash flow from diverse revenue streams, dominating the market. Here are some of the most innovative business models being employed by grocery delivery apps.
1. Single Store (Branded Retailer) Model
The single-store model works best for grocery retailers, supermarket chains, and local grocery retailers that want to fully digitize and integrate their operations with grocery delivery. In this model, the app acts as a single branded store and the app owner controls all aspects of store operations including inventory, pricing, and order fulfillment.
From an operational standpoint, this model provides the grocery retailer the best opportunity to maximize store margins, increase customer loyalty, maintain proprietary customer databases, and control the customer experience. Having predictable demand and an efficient supply chain works to the retailer’s advantage in the grocery delivery app model, as it enables rapid fulfillment of private-label products and loyalty rewards without sharing revenue with a third party.
2. Aggregator (Marketplace) Model
The aggregator model is the opposite of the single-store model. In this model, multiple grocery stores and supermarkets are included in a single grocery delivery app. This provides customers with the best grocery delivery options in the marketplace. The aggregator model marketplace app monetizes its services by charging grocery stores commissions, listing fees, and paid priority order placements for delivery.
This grocery delivery app model is the most popular in urban and hyperlocal marketplaces. The aggregator model works primarily because grocery stores and supermarkets provide multiple options that are equally convenient. From the grocery delivery app’s perspective, this model is advantageous because it does not have to manage inventory directly.
3. Subscription & Membership Model
By the end of 2026, grocery apps that use a subscription-based model will be extremely profitable. Customers pay fees, typically annually or monthly, for services such as personalized recommendations, free delivery, and exclusive discounts. This method sustains high customer loyalty and retention, increases lifetime value, and ensures the grocery app has a recurring revenue stream. This method is typically paired with either a single-store model or an aggregator model to optimize revenue.
4. Hyperlocal & On-Demand Delivery Model
On-demand delivery services that offer the fastest delivery times are the most effective. This model partners with local stores to deliver within 30 to 90 minutes. This is effective in urban areas where customers are more willing to pay for convenience. Revenue is made through surge pricing, delivery fees, and retailer partnerships. By 2026, hyperlocal models will use synchronized inventories, AI-driven demand forecasting, and improved routing to better serve customers.
5. Dark Store & Micro-Fulfillment Model
Digital grocery apps use dark stores to enhance their services. Dark stores are small warehouses dedicated to online grocery orders. With this, grocery apps obtain better revenue, faster service, and improved fulfillment. While most grocery apps consider this model, it is especially favored by venture-backed apps with aggressive goals for same-day or instant delivery and a desire to scale their services, even if it entails higher operational costs.
6. Advertising and Sponsored Listings Model
With the advancement of grocery apps, the advertising model will continue to expand. In-app promotions, featured listings, and sponsored product placements will become increasingly common. By 2026, advertising will become even more sophisticated, incorporating user behavior and purchase history, resulting in higher conversion rates and making this model highly lucrative for platforms with large user bases.
Why These Models Work in 2026?
Modern grocery delivery apps succeed because they combine:
- Multiple monetization streams (commissions, subscriptions, ads)
- Technology-driven efficiency (AI, analytics, automation)
- Consumer demand for speed, convenience, and personalization
For businesses investing in grocery delivery app development, selecting the right model or a hybrid of several is critical to building a platform that is not only functional but consistently profitable in today’s competitive market.
Step-by-Step Process to Develop a Grocery Delivery App
To successfully build a grocery delivery application, crossing stages will help you with long-term sustainability. In 2026, success will be measured by how well a platform integrates user experience, logistics, and monetization.
Step 1: Define the Business Model and Target Market
At this point, establishing the app’s initial business model is imperative. Is your platform a single-store, hyperlocal, aggregator, or subscription model? Also, be sure to clarify your target audience, delivery radius, pricing strategies, and your expected revenue. Setting this foundation will improve the user experience and outline the profitability of your grocery application.
Step 2: Finalize Core Features and User Roles
Identify the platform’s users and the number of user categories you need to support (e.g., Customer, Vendor, Delivery, Admin). Each of these will affect the final design of the core features of the delivery app. Purchasing, order tracking, and payment must be real-time and highly secure. Inventory and order analytics will need to be followed up with customized AI-based recommendations. Subscriptions, resale, and predictive ordering will be expected features.
Step 3: Choose the Right Technology Stack
Choosing the right tech stack for your grocery delivery app is essential to building a scalable app. A tech stack that incorporates cloud-native tech, AI, real-time databases, and secure payment gateways will make your app fast and always available. To balance traffic, a scalable backend will help your app align with seasonal demand and support multi-city growth.
Step 4: Design an Intuitive UI/UX
Order retention and frequency are influenced by the user experience. When users can navigate the app and complete a purchase with a fast, seamless interface, they are more likely to use it again. A dedicated developer can deliver strong returns by investing in high-quality user experience design and development.
Step 5: Develop, Integrate, and Test the Platform
In this stage, the iOS and Android applications, as well as the vendor and delivery partner dashboards and admin dashboards, are built. Integrations for payment processing, geolocation, push notifications, analytics, and more are added. This is the stage at which the app is most rigorously tested to ensure it is performant, secure, and reliable.
Step 6: Launch, Monitor, and Optimize
Once the feature is deployed, monitoring begins. Take note of user interactions, how effectively the feature performs, and how much revenue it is generating. Successful grocery delivery apps in 2026 will have rapidly incorporated data-driven performance improvements, feature rollouts, and machine learning insights to stay ahead.
Building grocery delivery apps in 2026 goes beyond just development. It is about creating a scalable, profitable ecosystem that can adapt to changing consumer demand. With this guide, businesses can build grocery delivery apps that prioritize user convenience and drive sustained growth.
Technology Stack Used to Build a Grocery Delivery App in 2026

Selecting appropriate technologies is important for developing an effective, scalable, and reliable grocery delivery app. User expectations will also need to be met. By 2026, grocery delivery applications will need to have competitive, real-time processing, AI-driven personalization, and secure payment processing.
1. Frontend Technologies
The user interface layer focuses on the customer/vendor/delivery partner user experience. React Native and Flutter are the two most popular options for cross-platform app development using a single codebase. Android and iOS are the preferred technologies for native performance and more sophisticated UI interactions.
2. Backend Technologies
Payment processing, user authentication, and overall order processing are the primary functions performed in the Back End layer. Systems integration for order processing will need to use node.js, Java (Spring Boot), and either FastAPI or Django for Python. A microservices architecture will be required to ensure interoperability, enabling independent scaling of payment and order processors.
3. Database & Real-Time Data
Delivery applications will require real-time information. Structured information will need to be organized using PostgreSQL and MySQL while unstructured information will be organized using MongoDB. Firebase and Redis will provide real-time updates to stock counts and order tracking.
4. Cloud Infrastructure
The development and global deployment of apps is enabled by scalable hosting, load balancing, and availability provided by platforms such as Google Cloud, Azure, and AWS.
5. Payments, Maps & Analytics
Payment gateways such as Stripe, Razorpay, and PayPal provide strong security and support a wide range of payment methods. Real-time tracking and route optimization are enabled by Google Maps APIs, while analytics provide insights into performance and user interactions.
With this technology, businesses can build a grocery delivery app that is secure, scalable, and future-ready for 2026.
Key Features Required to Build a Successful Grocery Delivery App
Building a successful grocery delivery platform for 2026 will require more than simple ordering and checkout. Users want fast, personalized service that is transparent and reliable. On the other hand, businesses need scalable, automated solutions that generate multiple revenue streams. The following are the must-have mobile app features aligns with current market expectations.
1. Customer App Features (User Experience Layer)
These features enhance user adoption, retention and frequency of orders. A well built customer app offers a valuable and convenient, quick and personalized service during the entire grocery shopping journey.
Smart Product Discovery & Search:
Users of grocery apps can already use AI-enhanced search to filter by brand, price, dietary requirements, and stock availability. Advanced features that further improve product search, and are not necessarily limited to grocery apps, include voice and image search, and personalized recommendations based on previous purchases.
Cart, Checkout & Payments:
An intelligent system that adds items to the cart streamlines the shopping experience and reduces cart abandonment. Several complementary features strengthen transaction security and offer multiple ways to complete payments. Customers may pay using UPI, credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and use the BNLP (buy now, pay later) option. Payment tokens are used to improve PCI compliance and fraud protection.
Order Scheduling & Smart Reordering:
Scheduled deliveries allow customers to coordinate grocery deliveries with their daily, weekly, or monthly schedules. Customers can also realize time savings with the repeat order feature, which leverages previous purchases, while subscription orders further enhance this, increasing customer retention.
Real-Time Order Tracking:
Customer satisfaction depends on the transparency of the delivery process. Customers appreciate having control over tracking with live GPS as well as having delivery ETA. Push notifications keep customers informed about the status of their orders and any potential delays. Furthermore, transparency and trust are built when customers can communicate with delivery staff via an in-app chat feature.
Reviews, Ratings & Trust Signals:
Customers depend on reviews and ratings when choosing stores, products, and delivery providers. Reviews are more impactful when they are linked to product purchases. Users to report and receive support for their problems, which strengthens their trust in the platform.
2. Delivery Partner App Features (Logistics Layer)
The delivery partner layer of grocery delivery apps is critical to speed, cost, and customer satisfaction. In 2026, the most advanced seamless tech delivery services will be the most successful.
Intelligent Order Assignment:
Artificial intelligence is used to assign orders to delivery partners based on distance, availability, and capacity. This optimizes delivery time, load balancing, and profitability.
Route Optimization & Navigation:
The delivery partner uses customized, traffic-integrated mapping systems to pinpoint the most efficient routes. Optimized routing is continuously provided to enhance delivery efficiency and performance across metropolitan and regional delivery areas.
Proof of Delivery:
Digital proof-of-delivery systems, particularly those that include one-time PINs and photos of the drop-off location, bolster accountability. These systems mitigate disputes between delivery partners, secure customer handovers, and enhance trust among customers, vendors, and the platform.
Earnings & Performance Dashboard:
All delivery partners receive a productivity and motivation score for services rendered on the platform. Delivery partners are incentivized to increase platform engagement and service quality through bonus structures, rewards, and visibility of performance scores.
3. Vendor / Store App Features (Supply Layer)
The vendor or store app forms the integrated grocery delivery network. It enables efficient supervision and coordination of supermarket, local retailer, and dark store activities. By 2026, this layer aims to provide real-time visibility, quick fulfillment, and revenue maximization.
Inventory & Pricing Management:
The automatic synchronized inventory will help all vendors avoid order cancellations, and keep their stock status updated across multiple stores. Vendors using inventory optimization tools can keep competitors at bay and maintain profit margins by capturing and adjusting their automated pricing strategies.
Order Processing & Fulfillment:
With this centralized system, vendors will enjoy more flexibility, as they can accept and reject orders, update packing, and, order status. Higher service reliability and faster order fulfillment will be delivered to high-value customers, who will have their orders prioritized.
Promotions & Sponsored Listings:
In-app promotional tools enable vendors to customize and manage their own discounts, seasonal promotions, and flash sales. Creating sponsored listings will help boost revenue for stores and for the platform by keeping items at the front of the app and increasing sales.
4. Admin Panel Features (Control & Growth Layer)
The grocery delivery platform has an admin panel that monetizes data and keeps the platform running systemically. This layer will be crucial to overseeing the business’s ecosystem as it scales in 2026.
Centralized Dashboard:
A unified dashboard displays real-time updates for orders, sales, vendors, and deliveries for all locations. While administrators, vendors, and support teams have access to different dashboard features based on their roles, this enhances security and operational visibility. This is called role-based access.
Analytics & Business Intelligence:
Advanced analytics help understand customer activity, order placement, and buying behavior. Reporting on sales performance, and forecasting demand, aids companies in optimizing inventory and marketing strategies. Analysis on conversion, customer retention, and churn contributes to sustained growth.
Monetization & Revenue Management:
Platforms that offer flexible monetization controls can set individual-store commission rates or category-specific commissions. Managing subscription plans, delivery fee policies, and control over sponsored products and service ads enables diverse, stable revenue streams.
Content & Notification Management:
Engagement is reinforced, repeat orders are driven, and campaign performance improves through personalized push notifications. Modifications to promotional content, campaign banners, and in-app notifications are made through dynamic content editing tools.
5. Advanced & Future-Ready Features (2026 Differentiators)
These are the features that define market leaders versus the average app.
- AI-enabled demand forecasting & inventory management
- Micro-fulfillment & dark store integration
- Sustainability (eco-packaging, green delivery)
- Hyperlocal personalization & geolocation
- Cloud-native for high scalability
Why Will This Feature Framework Work In 2026?
This framework is viable because grocery delivery apps rely on automation, AI, and rapid data processing rather than manual workflows. Customer experience becomes more stickier and the frequency of orders is driven by personalization. High customer retention is supported by a diverse set of app monetization models (subscriptions, commissions, sponsored listings, etc.).
This modular cloud architecture is built for optimal efficiency and renewed reliability. Thus, from a business standpoint, it promotes scaling operations seamlessly. This feature framework ensures the grocery delivery app you wish to develop, in 2026, is competitive, functional, and profitable, with the ability for long-term growth.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Grocery Delivery App in 2026?
Development time for grocery platforms is influenced by feature count, complexity, and other objectives, such as long-term scalability. Development time for grocery apps depends on the product release strategy. If an MVP is being launched, development time ranges from a couple of months to a year; for full-scope products, it can be an additional year. The development of grocery apps in 2026 will likely take longer if the apps incorporate AI, real-time logistics, and cloud technologies.
For most startups testing the market with an MVP, it is typical to include only the core features of grocery delivery apps, like browsing, cart, payment, and order tracking. In contrast, enterprise grocery delivery apps are built to optimize monetization of their development time by customizing features such as enhanced analytics, recurring revenue subscriptions, and multi-vendor capabilities.
Given the aforementioned factors, expect the realization of 2026 development timelines as specified below:
| App Type | Key Scope | Estimated Timeline |
| MVP Grocery App | Core user features, basic admin panel | 3–4 months |
| Mid-Level App | Multi-vendor, delivery partner app, analytics | 5–7 months |
| Advanced App | AI, subscriptions, dark store support | 8–10 months |
Understanding how to develop a grocery delivery app with the right scope helps businesses launch faster while staying scalable and future-ready.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Building a Grocery Delivery App
When companies develop a grocery delivery app, the primary focus is often on features and aesthetics. However, a large portion of grocery delivery apps fail due to strategic and technical issues that arise during app development, not due to a lack of demand. In 2026, the primary factors determining the sustainability of a grocery delivery app will be scalability, operational efficiency, and monetization.
The following list of app development challenges will help you build a sustainable grocery delivery app and avoid costly, time-consuming mistakes.
1. Ignoring Scalability from Day One
Most companies selling grocery delivery apps overlook app scalability. After launch, the app is designed to scale with demand; if it is successful and sees growing demand, it will scale accordingly.
2. Underestimating Real-Time Inventory Management
Because the app lacks a system to manage canceled orders in real time, orders will be automatically canceled, resulting in a poor experience for customers and a loss of trust among customers, vendors, and delivery partners.
3. Poor User Experience and Complicated Checkout
The overall experience the customer has with the app will be determined in part by how smoothly the user navigates the interface.
4. Weak Logistics and Delivery Optimization
Several factors can degrade the user experience customers receive when using the platform, directly resulting from the platform’s logistical and operational infrastructure.
5. Overlooking Monetization and Data Analytics
Revenue models and early-stage analytics are essential for growth. Without them, businesses lack sufficient information to make critical long-term decisions on pricing, subscriptions, promotions, and overall revenue potential.
Conclusion
Successful construction of grocery platforms in the current on-demand economy requires much more than just an app idea; it also requires the right technology, strategy, and execution. To understand how to build a grocery delivery app in 2026, one must consider intelligent logistics, scalable architecture, and user experiences designed to drive high engagement. Every decision, from selecting the right business model and defining the must-have features of a grocery delivery app to picking a technologically advanced stack, influences profitability and performance.
With increased competition, businesses creating grocery delivery apps need to focus on personalization, real-time updates, and seamless monetization to stand out. Investing in a knowledgeable development team helps you launch not just faster, but smarter. Grocery delivery apps, with the right strategy, can become consistent revenue generators and flexible to adapt to the ever-changing digital economy.
FAQ’s
Q1. How much does it cost to create a grocery delivery app?
Ans. The cost to build a grocery delivery app depends on features, platforms, and complexity. In 2026, grocery delivery app development costs typically range from $10,000 to $1,00,000+.
Q2. How long does it take to build a grocery delivery app?
Ans. An MVP can take 3–4 months, while a full-scale solution with advanced grocery delivery app features may take 8–10 months, depending on customization and integrations.
Q3. What are the must-have features in a grocery delivery app?
Ans. Core features include product search, cart, secure payments, real-time tracking, inventory management, delivery partner integration, analytics, and personalization for better retention and monetization.
Q4. Are grocery delivery apps profitable in 2026?
Ans. Yes, grocery delivery apps to make money succeed through subscriptions, commissions, delivery fees, sponsored listings, and data-driven personalization that increases order frequency and customer lifetime value.
Q5. Can I scale my grocery delivery app after launch?
Ans. Absolutely. Using cloud-native architecture, modular development, and real-time data systems allows businesses to scale their grocery delivery app across cities, vendors, and users seamlessly.