The shifting landscape of customer expectations involves not only the speed of order fulfillment but also the logistics of seamless, automated, same-day order fulfillment. This market space intertwines with the ever-increasing demand for global online retail sales. Most retailers and logistics companies are experiencing immense pressure to develop innovative strategies for last-mile delivery while controlling operational costs.
The drone package delivery market is projected to grow from about USD 0.7–0.99 billion in the mid-2020s to roughly USD 4.6–4.78 billion by 2030, at CAGRs of around 37%. This rapid market growth is driven by operational efficiencies, autonomous technologies, and more flexible regulatory environments, which are reshaping the delivery landscape.
This guide describes the various systems that comprise a delivery drone, the processes used to complete drone deliveries, and the systems that are making a positive impact in different sectors. Delivery drone systems are making a positive impact across sectors such as retail, healthcare, and industrial logistics.
This guide provides a framework for understanding various delivery drone systems and their long-term application potential, while also offering insights for investors and businesses exploring a professional drone delivery app development service to support scalable drone delivery operations.
What Is Drone Delivery?
Drone delivery is a subfield of logistics that uses drones to deliver goods without a human pilot. That means no human can be on board a drone delivering an item. This is like the drone delivery systems of the future are designed for speed, with a focus on logistics for that last mile. That is, their goal is to shift the focus of delivery to last-mile logistics systems, which are traditionally very ground-dependent, and serve areas that are less easily accessible by ground delivery systems.
As far as systems go, drone deliveries encompass a great deal of cutting-edge technology. Drones can be programmed to avoid obstacles and complete deliveries using stored information from previous deliveries. Drones also have onboard sensors that enable real-time communication and flight control, allowing them to fully manage the delivery process without human intervention. Once a delivery is assigned to a drone, it can plan its own route and complete the delivery. With the advent of new technology, drone deliveries are shifting from early-stage of app testing to full commercial use across different sectors.
How Does Drone Delivery Work?
Drones and Drone delivery are exciting applications that enhance customer experiences by employing numerous modern technologies and sophisticated systems. Drones use integrated software, automated control, and real-time processing to deliver autonomously, safely, and efficiently. The delivery process begins when the customer places an order online.
The drone operator or delivery service then uses automated software to generate a command and schedule the delivery. The drone is equipped with a series of onboard systems and data communication mechanisms, including GPS, sensors, and control systems, which deliver data to the service operator. The delivery service uses a ground control platform to monitor the delivery.
The service uses data to deliver systems-level ground and air route control, airspace systems, and autonomous ground delivery systems, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of deliveries. This simple model illustrates all the systems and technologies involved in customer drone delivery. The objective of the model is to explain the systems that enable drone delivery services and why they are important.
Drone Delivery Process: Step-by-Step Explanation
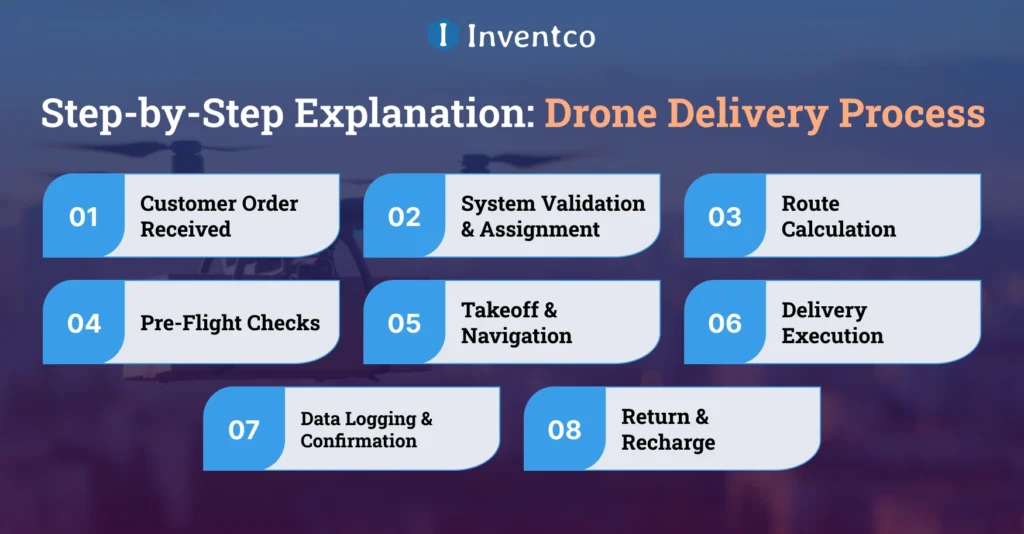
The use of modern technology, automation, and operational checks must be integrated at each stage of the app development process to deliver a complete, functional customer service experience. The real-life applications of these systems form the basis for the services they offer customers. The systems deliver services continuously and at a high service level to the customer.
1. Customer Order Received
When customers place orders on mobile apps or use e-commerce platforms, the process for drone delivery begins. This triggers the collection of important data for the delivery system, including the pickup and delivery addresses, package weight, and the requested delivery time window.
2. System Validation & Assignment
When the order is received, the system streamlines operational verification. It reviews delivery distance, weight, service area, legal delivery regulations, drone availability, and the best drone for the delivery based on those parameters.
3. Route Calculation
Upon drone assignment, the system uses the governing rules of the specific airspace, obstacles and environmental conditions, and geospatial data to create the most efficient route for the drone to comply with regulations, minimize flight time, and reduce delivery operational risk.
4. Pre-Flight Checks
Automated diagnostics, such as testing the communication link, securing the payload, sensor calibration, and battery health verification are done prior to takeoff. Only when the drone passes all of the operational thresholds, is it cleared for autonomous dispatch.
5. Takeoff & Navigation
The drone will take off and start navigating the defined path. While in transit, the drone analyses data from GPS, onboard sensors, and computers to avoid collisions and adjust its route and altitude to remain stable throughout the flight.
6. Delivery Execution
When the drone reaches the specified location, it will either land and deliver the package to a designated landing zone or use a tether to drop it. The tether will ensure the package is not damaged and that delivery will not disrupt bystanders or the surrounding area.
7. Data Logging & Confirmation
The system will automatically upload flight, delivery, and operational statistics after the package has been delivered. Data will be logged for tracking and compliance, and the customer and the remote operator will receive real-time notifications to stay up to date. This process will allow the system to optimize data tracking and reporting.
8. Return & Recharge
After a delivery is completed, the drone will navigate to the nearest charging station or its designated base. The drone will undergo a system update and have its battery charged. After these tasks, the drone will either be assigned to a new delivery or flagged for any required app maintenance.
Where Drone Delivery Is Used Today?
As of today, drone delivery services are moving beyond pilot programs and are being used in all locations where goods must be delivered quickly and efficiently.
1. E-commerce & Retail
The use of drones in e-commerce and retail delivery allows retailers to shift the last mile of the delivery process, improving efficiency for lower-weight, higher-volume purchases, particularly in highly populated urban areas where frequent, significant delays occur due to vehicular congestion.
2. Healthcare & Medical Logistics
Healthcare and medical services use drones to facilitate inter-facility transport of supplies, including medicines, vaccines, diagnostic tests, emergency medical supplies, and equipment, to support time-sensitive medical services in urban and even outlying, more remote areas.
3. Disaster Relief & Emergency Response
In areas that have been affected by disasters, where the road and transport systems have been damaged or are not accessible to worsen the delivery of essential items, including medicines, food, and tools to capture and maintain communication, delivery by drone can assist in enabling the delivery of goods more quickly than by other means.
4. Industrial & Enterprise Logistics
Industrial drone delivery logistics have recently been used to move goods stored in large industrial warehouses, ports, and manufacturing facilities, making inventory management more efficient and cost-effective and reducing the amount of manual labor required.
5. Food & Grocery Delivery
Drone services are being used to reduce delivery times in restaurants and grocery stores, maintain food freshness, and meet consumer needs.
6. Rural & Hard-to-Reach Locations
Drone delivery services are successfully closing gaps in logistics in remote and rural areas and overcoming major obstacles in remote and high mountain regions that limit and slow traditional delivery services, delivering at lower cost and with higher reliability.
What are the Benefits of Drone Delivery?
Investor interest and the founding of companies specializing in drone delivery are driven by the resolution of ever-present last-mile problems and by the promise of scalable logistics benefits. At the following list of six benefits, each of which is explained succinctly.
1. Faster Delivery Times
Delivery by drone is free of delays caused by vehicles and road-traffic interruptions in the current system of fixed traffic installations. The time saved in delivery is particularly beneficial for the speed of delivery, which is urgent in the context of time, in the urban, suburban, and even remote areas of the service.
2. Lower Operational Costs
The dependence on the road and the vehicles that are powered by fuel, and the trucks that are driven by drivers, and the fleets of trucks, are all decreased by delivery by drone. The long range of operational costs has decreased. The costs associated with labor are decreased and the delivery of items is consistent and predictable, which improves overall operational costs as delivery is automated for more than one flight.
3. Improved Accessibility
Drones can engage with services in more remote areas. Human cost and time delays in vehicles are avoided in delivery services, thereby increasing the range of services that can be offered without grounding and reducing investment.
4. Reduced Carbon Footprint
Electrically powered delivery vehicles equipped with delivery drones produce lower emissions. The environmental impact and sustainability goals have improved. Compliance with increasing regulations is ensured, while consumers and companies focus on delivering soon.
5. Scalable Infrastructure
Businesses can improve drone fleet operations without making significant infrastructure changes. Adding drone units allows companies to expand their delivery capacity without incurring the exorbitant costs of additional transportation and warehousing resources.
6. Enhanced Customer Experience
Customers are satisfied with faster, more trackable deliveries. Meeting customer expectations with faster delivery and transparency strengthens customer trust in the brand, increasing loyalty.
Challenges & Limitations of Drone Delivery
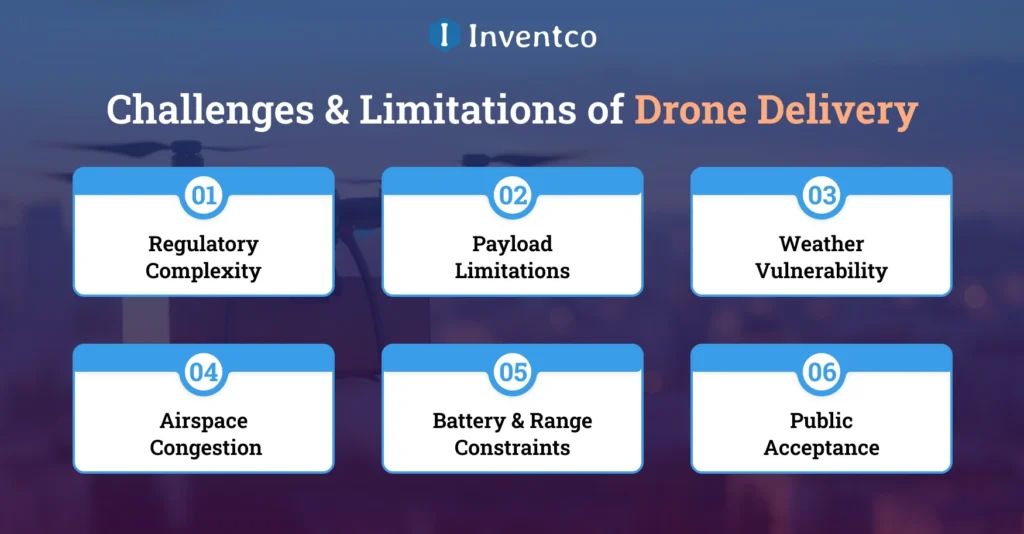
Although drone delivery has the potential to be highly useful, understanding the app development challenges it faces will aid the development of future plans to ensure successful long-term operations.
Below are some of the challenges businesses will need to overcome to effectively incorporate drone delivery at an operational level:
1. Regulatory Complexity
To use a drone for any type of operational delivery, the business will need to be up to date with the country’s aviation rules. There are multiple rules that must be followed, including, but not limited to, operational airspace, delivery permits, flight altitude, and the delivery of packages that meet the beyond-visual-line-of-sight criteria.
2. Payload Limitations
Most currently operating delivery drones can only carry a limited amount of weight. This greatly reduces the versatility of the delivery operational capabilities of the drone in any business and the type of packages that can be delivered in order to keep the operational capabilities of the delivery drones at a satisfactory level.
3. Weather Vulnerability
Climatic challenges pose the greatest potential concerns for the delivery of drones’ operational capabilities. Weather patterns like heavy rain, extreme cold, and wind can affect the drone’s ability to fly fully operational, as they may inhibit its performance. If the delivery will take place in changing climate areas, this will only pose an even greater challenge for the operational climate.
4. Airspace Congestion
The use of drones is expected to increase, so the number of drones in the air will increase. Separate rules and regulations will need to be in place to maintain a safe operational airspace for delivery drones.
5. Battery & Range Constraints
The aerial drone’s battery capacity limits its flight duration and range. This requires implementing charging stations or return-to-base operations. Such a measure can impact the overall efficiency of the drone system, especially in large service areas.
6. Public Acceptance
Public concerns about drone noise, safety, and data privacy can affect the acceptance of drone delivery. Thus, trust within the community, along with the transparency of the operations, are key to the potential acceptance and future regulation of the drone delivery systems.
Future of Drone Delivery Technology

The future of drone delivery relies on automation, the integration of delivery drones into air traffic, and advances in air traffic control automation to improve efficiency and safety across all aspects of drone delivery.
1. Enhanced Autonomy
The drones of tomorrow will have more sophisticated systems that enable autonomous decisions, such as rerouting to avoid obstacles or changing delivery addresses in real time, to improve operational efficiency, safety, and reliability.
2. UAM Air Traffic Systems
The future will see integrated air traffic control systems that will manage Drones and other flying vehicles as they share airspace. These systems will manage real-time access to airspace and control drone traffic to optimize congested urban and suburban areas.
3. Swarm Operations
The future will see advanced swarm technology that enables the coordination of larger groups of drones and the optimization of delivery routes and workloads to improve the overall efficiency of the delivery system, especially in high-traffic areas.
4. Next-Generation Batteries & Power Systems
Commercial drones will become more capable of extended flight operations as advanced battery technology and alternative power systems continue to be refined. Drones will be less restricted to areas of operation, expanding the scope of drone delivery.
5. Integration with IoT Ecosystems
Strengthening the drone delivery system will accelerate the adoption of these innovations in large-scale, practical applications, making it essential to carefully choose a drone software development company that can support scalability, compliance, and long-term operational success.
Strengthening the drone delivery system will accelerate the adoption of these innovations in large-scale, practical applications.
Conclusion
It is now essential for founders and investors building next-gen logistics companies to understand the business case for drone delivery. Beyond technology, drone delivery systems are changing how the last mile is fulfilled. In almost every domain and geography, we are seeing faster delivery times, wider service areas, and more productive operations.
With the accelerating pace of adoption, businesses that understand the drone delivery process are best positioned to develop scalable and compliant delivery systems. Drone delivery can help meet customer needs and operational demands while giving businesses a competitive advantage by optimizing supply chain performance and expanding into new markets.
FAQ’s
Q1. How does a delivery drone work?
Ans. A delivery drone operates using GPS navigation, onboard sensors, and automated software to plan routes, avoid obstacles, and reach delivery locations autonomously while carrying packages within defined payload, distance, and safety limits.
Q2. What is drone delivery?
Ans. Drone delivery is the use of unmanned aerial vehicles to transport goods through the air, enabling faster, more efficient logistics operations by reducing dependence on road traffic and traditional delivery infrastructure.
Q3. What are the limitations of drone delivery?
Ans. Drone delivery faces limitations such as regulatory restrictions, limited payload capacity, weather sensitivity, airspace coordination challenges, and battery range constraints, which can impact scalability and consistent operations across regions.
Q4. Are drone deliveries safe?
Ans. Drone deliveries can be safe when supported by strong regulations, automated flight controls, real-time monitoring, and collision-avoidance systems. However, safety standards continue to evolve alongside technology and regulatory frameworks.
Q5. Can drones carry heavy packages?
Ans. Most delivery drones are designed for lightweight to medium payloads. Carrying heavier packages remains limited by battery capacity, flight stability, and safety considerations, though future advancements may increase lifting capabilities.
Q6. What industries benefit most from drone delivery?
Ans. Industries such as healthcare, e-commerce, food delivery, disaster response, industrial logistics, and rural services benefit most by leveraging faster delivery times and improved access to difficult locations.
Q7. How far can delivery drones typically travel?
Ans. Delivery drone range depends on battery capacity, payload weight, and weather conditions. Most commercial drones operate within short to medium distances, optimized for last-mile and point-to-point delivery use cases.
Q8. Is drone delivery suitable for urban areas?
Ans. Drone delivery can be effective in urban environments when supported by proper airspace management, designated landing zones, and noise controls, helping businesses overcome traffic congestion and improve last-mile efficiency.





